Introduction:
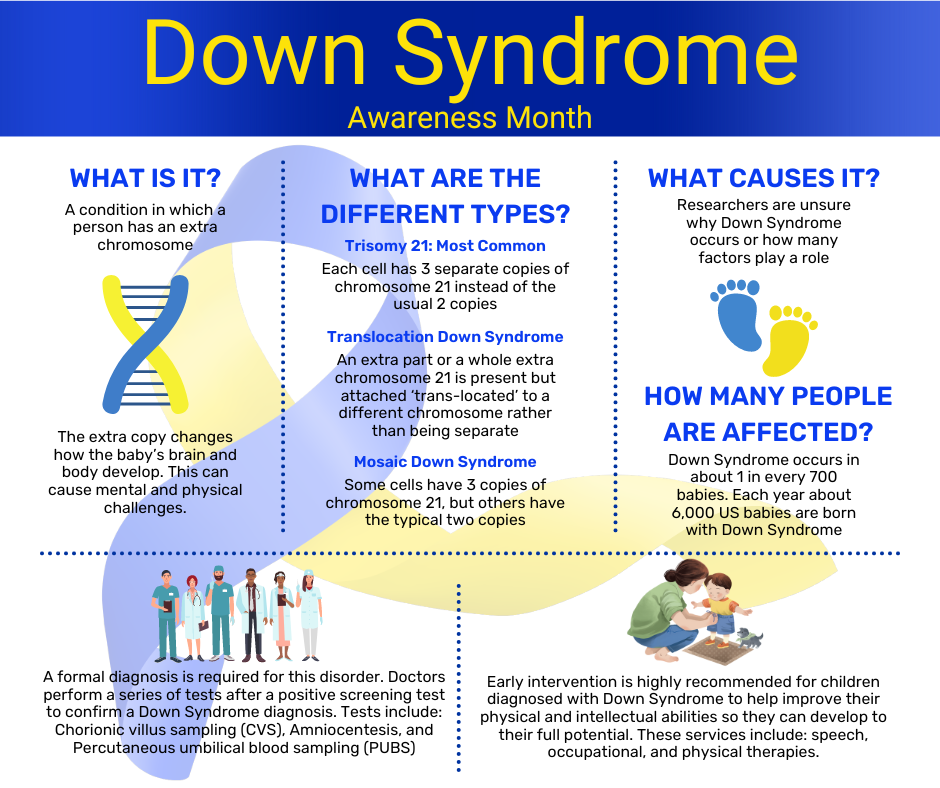
Down syndrome is a genetic situation that takes place while there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. Named after the British doctor John Langdon Down, who first described the syndrome in 1866, Down syndrome is one of the maximum commonplace genetic issues, affecting approximately 1 in seven hundred live births worldwide. No matter its occurrence, there may be still a large amount of incorrect information and misconceptions surrounding Down syndrome. This article targets to provide a comprehensive expertise of Down syndrome, have a good time the particular skills and qualities of individuals with Down syndrome, and endorse for a greater inclusive society.

Understanding the Genetic Basis:
Chromosomes are systems within cells that comprise genetic records. Normally, people have 23 pairs of chromosomes, and every figure contributes one chromosome to every pair. In the case of Down syndrome, there’s an additional reproduction of chromosome 21, leading to a total of 3 copies rather than the usual two. This greater genetic cloth disrupts normal improvement and results in the function capabilities and fitness issues associated with the syndrome
Physical and Developmental Characteristics:
Individuals with Down syndrome often share a few commonplace physical features, inclusive of almond-shaped eyes, a flat facial profile, and a short neck.They may also experience developmental delays in areas such as speech and motor skills. However, it is crucial to recognize that each person with Down syndrome is unique, and the degree of developmental delay can vary widely.

Health Considerations:
People with Down syndrome are at an accelerated chance for positive health situations, together with heart defects, breathing problems, and thyroid troubles. Regular medical check-ups and early interventions can help address these concerns and improve overall health outcomes. Advances in medical care and increased awareness have significantly improved the life expectancy and quality of life for individuals with Down syndrome.
Inclusive Education and Employment:
Creating an inclusive society involves providing equal opportunities for education and employment. Many people with Down syndrome can lead enjoyable lives when given the proper support and sources. In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on inclusive schooling, in which college students with Down syndrome are included into mainstream lecture rooms, fostering social interaction and information amongst peers.
Employment opportunities for individuals with Down syndrome have also expanded, with organizations recognizing the unique skills and perspectives they bring to the workplace. Advocates argue that embracing diversity benefits society as a whole, fostering creativity, empathy, and a richer tapestry of experiences.
Promoting Social Inclusion and Breaking Stereotypes:
Despite progress, individuals with Down syndrome may still face stereotypes and stigmas. It is vital to mission these misconceptions and promote a greater inclusive society. By using emphasizing the abilities, talents, and contributions of individuals with Down syndrome, we are able to smash down limitations and foster a culture of recognition and appreciation.
Types of Down Syndrome:
Down syndrome is primarily associated with an extra copy of chromosome 21, but there are different types and variations of this genetic condition. Knowledge the varieties of Down syndrome can offer precious insights into the unique genetic mechanisms at play and their implications for individuals affected by the syndrome.
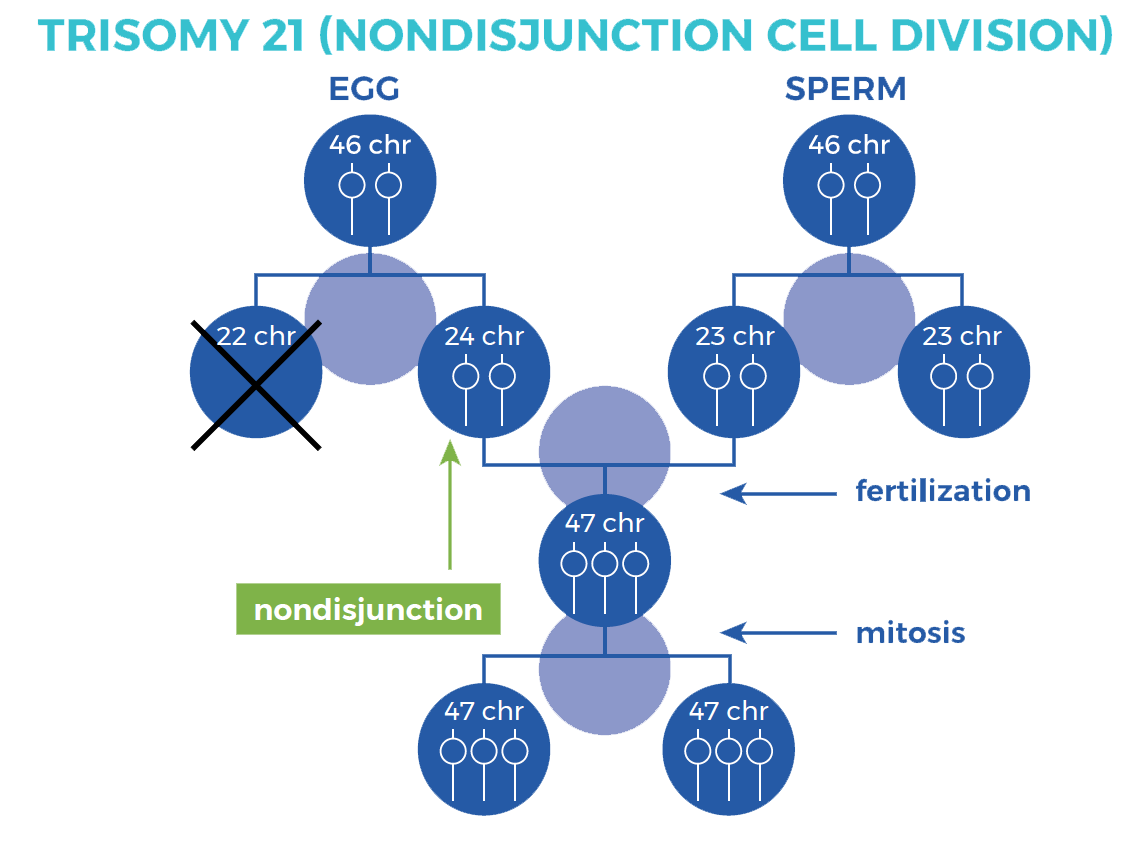
- Trisomy 21 (Non-disjunction):
- Description: This is the most common type of Down syndrome, accounting for approximately 95% of cases. It takes place while there may be a failure inside the separation (disjunction) of chromosome 21 in the course of the formation of eggs or sperm, main to a further copy within the resulting embryo.
- Genetic Mechanism: Trisomy 21 consequences from nondisjunction throughout the preliminary cell division after fertilization.
- Translocation Down Syndrome:
- Description: Translocation Down syndrome accounts for about 3-4% of cases. Unlike trisomy 21, the extra chromosome 21 is attached or translocated onto another chromosome, typically chromosome 14. This can be an inherited condition, where a parent carries a balanced translocation of chromosomes.
- Genetic Mechanism: On this kind, the extra genetic material continues to be gift, but it’s miles attached to another chromosome.
- Mosaic Down Syndrome:
- Description: Mosaic Down syndrome is noticeably rare, happening in approximately 1-2% of cases. It consequences from a random mistakes in the course of cell division after fertilization, leading to a aggregate of cells with an average chromosomal remember and cells with a further reproduction of chromosome 21.
- Genetic Mechanism: Some cells in the body have the usual chromosomal makeup, while others have the additional chromosome 21.
Conclusion:
Personal syndrome is part of the rich tapestry of human range. At the same time as individuals with Down syndrome might also face specific demanding situations, they also convey a wealth of pleasure, resilience, and specific views to the arena. Via improved awareness, training, and advocacy, we can create a society that embraces and celebrates the strengths and talents of every character, no matter their genetic make-up.