Introduction:
Stress is an inevitable part of life, affecting individuals in various ways and at different stages. While a certain amount of stress can be motivating and essential for survival, chronic stress can have detrimental effects on physical and mental well-being. In this article, we will explore the concept of stress, its causes, and effective strategies for managing and mitigating its impact.
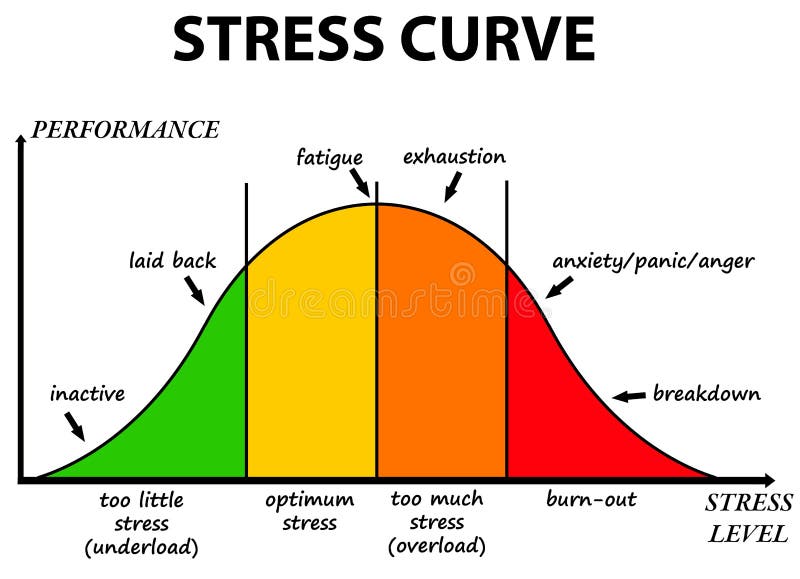
I. What is Stress?
Stress is the body’s natural response to a perceived threat or challenge. It triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, preparing the body for a “fight or flight” response. While this response is crucial for survival in certain situations, prolonged exposure to stressors can lead to health problems.

II. Common Causes of Stress:
- Workplace Pressure:
- High workloads, tight deadlines, and job insecurity can contribute to stress in the workplace.
- Personal Relationships:
- Conflicts, breakups, or strained relationships with family and friends can be significant stressors.
- Financial Concerns:
- Money-related issues, such as debt, unemployment, or financial instability, can lead to chronic stress.
- Health Challenges:
- Chronic illnesses, injuries, or the health concerns of a loved one can be emotionally taxing.
- Life Transitions:
- Major life events like moving, marriage, divorce, or the death of a loved one can induce stress.

III. The Impact of Stress on Health:
- Physical Effects:
- Chronic stress can contribute to headaches, muscle tension, digestive problems, and cardiovascular issues.
- Mental Health Consequences:
- Stress is linked to anxiety disorders, depression, and other mental health issues.
- Cognitive Impairment:
- Prolonged stress can impair memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities.
IV. Effective Stress Management Strategies:
- Mindfulness and Meditation:
- Practices that promote mindfulness, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress.
- Regular Exercise:
- Physical activity releases endorphins, which act as natural mood lifters and stress relievers.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Adequate sleep, a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine contribute to overall well-being.
- Social Support:
- Maintaining strong social connections and seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can help alleviate stress.
- Time Management:
- Prioritizing tasks, setting realistic goals, and learning to say no can prevent feelings of overwhelm.
- Hobbies and Leisure Activities:
- Engaging in activities you enjoy can provide a necessary break from stressors and promote relaxation.
V. Seeking Professional Help:
- Therapy:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can help individuals develop effective coping mechanisms.
- Medication:
- In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms of stress and related mental health conditions.

Conclusion:
Recognizing and addressing stress is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By understanding the sources of stress and adopting effective coping strategies, individuals can build resilience and lead more balanced, fulfilling lives. It’s important to remember that seeking support from friends, family, or professionals is a sign of strength, and there is a range of resources available to help manage stress effectively.

