Introduction
Phobias, a type of anxiety disorder, are intricate manifestations of fear that can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily life. From the common fear of spiders (arachnophobia) to more complex anxieties like agoraphobia, phobias come in various forms, affecting millions of people worldwide. This article delves into the nature of phobias, exploring their origins, symptoms, and potential strategies for overcoming these often debilitating fears.
Understanding Phobias
A phobia is an intense, irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity. The fear associated with a phobia is disproportionate to the actual threat posed by the feared entity. Phobias can be categorized into specific phobias, social phobias, and agoraphobia.
- Phobia is an intense, irrational fear of a selected object, situation, or activity. The fear associated with a phobia is disproportionate to the real danger posed by using the scary entity. Phobias may be categorised into specific phobias, social phobias, and agoraphobia.
- Particular Phobias: those are centered on precise items or conditions, such as heights (acrophobia), flying (aviophobia), or animals (zoophobia).
- Social Phobias: additionally known as social anxiety disease, this involves an overwhelming fear of social conditions and interactions.
- Agoraphobia: Individuals with agoraphobia fear and avoid places or situations where escape might be difficult or help unavailable, such as crowded areas or public transportation.

Types of Phobia
Certainly! Phobias can happen in various paperwork, encompassing a huge range of fears. Here are a few commonplace kinds of phobias:
- Acrophobia: Fear of heights.
- Arachnophobia: Fear of spiders.
- Astraphobia: Fear of thunder and lightning.
- Claustrophobia: Fear of confined or enclosed spaces.
- Cynophobia: Fear of dogs.
- Nyctophobia: Fear of darkness or the night.
- Ophidiophobia: Fear of snakes.
- Social Phobia (Social Anxiety Disorder): Fear of social situations, interactions, or judgment from others.
- Agoraphobia: fear of conditions in which break out may be difficult, consisting of crowded locations or open areas.
- Glossophobia: worry of public speakme.
- Trypophobia: worry of irregular patterns or clusters of small holes or bumps.
- Hemophobia: Fear of blood.
- Thanatophobia: Fear of death or the fear of dying.
- Claustrophobia: Fear of needles or injections.
- Nomophobia: Fear of being without a mobile phone or being unable to use it.
- Germophobia: Fear of germs or contamination.
- Mysophobia: Fear of dirt or filth.
- Triskaidekaphobia: Fear of the number 13.
- Xenophobia: Fear or aversion to strangers, foreigners, or anything unknown or foreign.
- Ablutophobia: Fear of bathing or washing.
It’s important to note that phobias can vary widely in severity, and their impact on an individual’s life can differ. Treatment options, including therapy and medication, are available for those seeking assistance in managing and overcoming their phobias.

Causes of Phobias
Phobias can develop for various reasons, often stemming from a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Traumatic experiences, such as a frightening incident involving the feared object or situation, can contribute to the development of a phobia. Moreover, a circle of relatives history of anxiety issues may also increase the probability of growing a phobia.
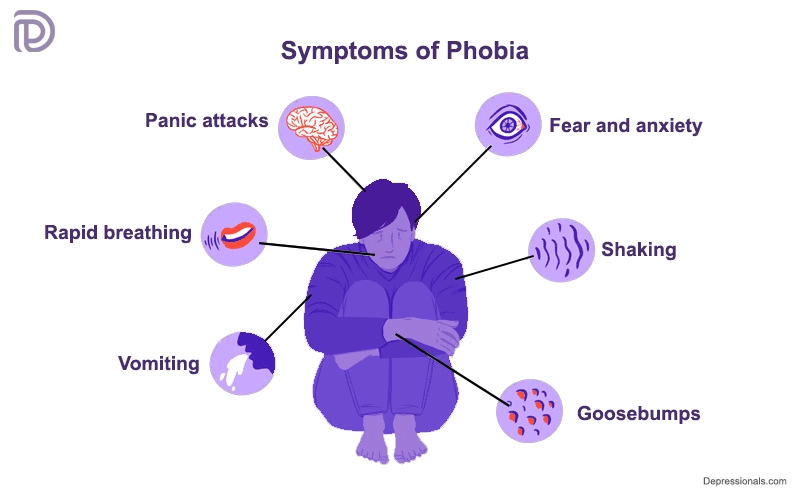
Symptoms of Phobias
The symptoms of phobias can vary widely, but common signs include:
- Intense fear and anxiety when exposed to the phobic stimulus.
- Rapid heartbeat, trembling, and shortness of breath.
- Avoidance of the feared object or situation.
- Difficulty functioning normally due to the fear.
Coping Strategies for Phobias
- Gradual Exposure: Exposure therapy involves gradually and safely facing the feared object or situation. This process helps desensitize individuals to the source of their phobia, reducing anxiety over time.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapeutic approach for phobias. It specializes in identifying and tough bad concept patterns related to the terror, helping people broaden healthier coping mechanisms.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage anxiety associated with phobias.
- Medication: In a few instances, remedy, along with anti-anxiety capsules or beta-blockers, can be prescribed to relieve signs. But, medicinal drug is often used at the side of therapy.
Overcoming Phobias
Overcoming a phobia is a gradual process that requires dedication and persistence. Searching for professional assist from intellectual fitness professionals, along with psychologists or psychiatrists, is important. Therapy sessions can provide tailored strategies and support, empowering individuals to confront and manage their fears.
Conclusion
Phobias are complex and deeply rooted fears that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Recognizing the signs, understanding the underlying causes, and employing effective coping strategies are crucial steps toward overcoming these fears. With the right support and interventions, individuals can reclaim control over their lives and navigate the world with newfound confidence and resilience. In case you or a person is suffering with a phobia, in search of professional help is a proactive and empowering step in the direction of a life loose from the shackles of irrational fears.

