Introduction:
In the realm of mental health treatment, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stands out as a highly effective and widely practiced approach. Developed in the 1960s by Dr. Aaron T. Beck, CBT has since evolved into a versatile therapeutic method embraced by mental health professionals worldwide. This article ambitions to offer a comprehensive overview of Cognitive Behavioral remedy, exploring its ideas, strategies, and applications.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy:
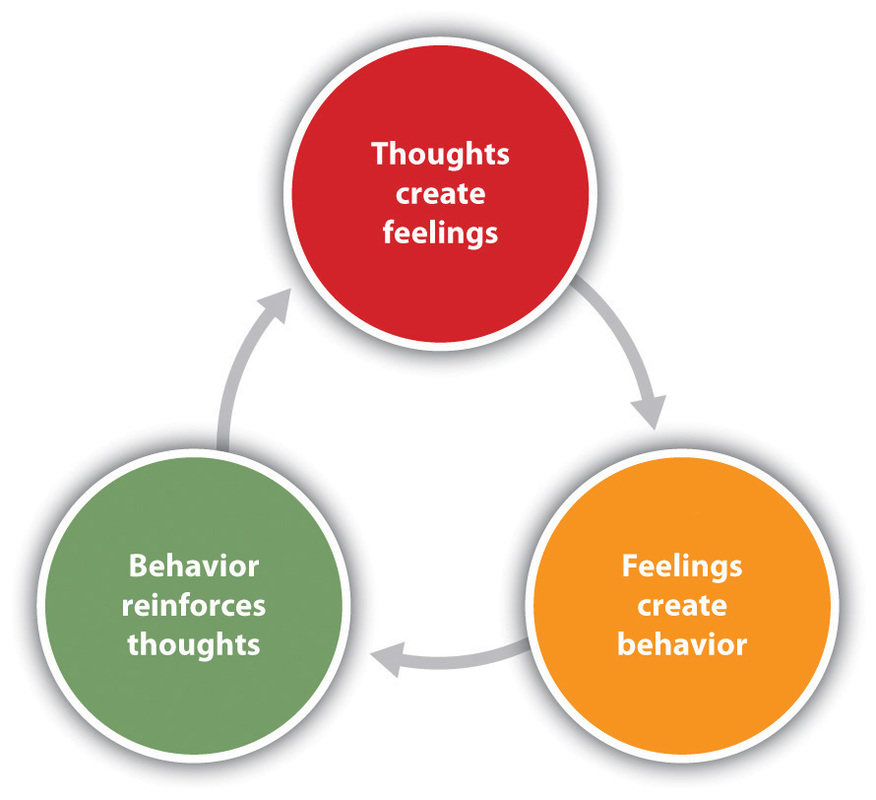
Cognitive Behavioral therapy is a purpose-orientated and evidence-based psychotherapeutic technique that specializes in the relationship between mind, feelings, and behaviors. The essential principle of CBT is that our mind, ideals, and perceptions notably affect our emotions and actions. By identifying and modifying negative thought patterns, CBT aims to bring about positive changes in behavior and emotional well-being.
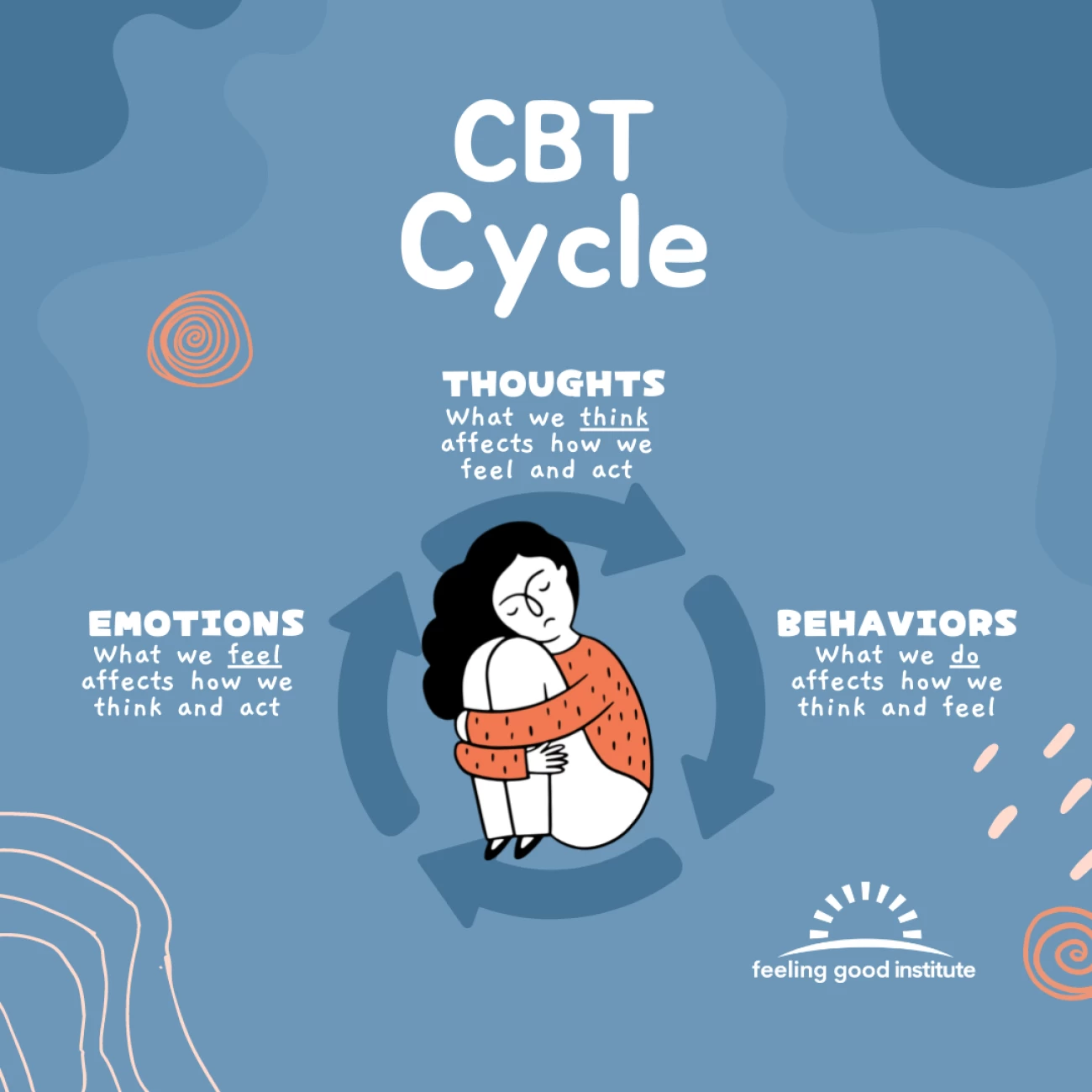
Key Principles of CBT:
- Cognitive Restructuring: CBT emphasizes the identity and restructuring of distorted or irrational thoughts. Sufferers discover ways to apprehend and task terrible wondering patterns, replacing them with extra balanced and sensible thoughts.
Behavioral Activation: This issue involves encouraging individuals to have interaction in activities that convey them joy or a sense of accomplishment. - Exposure Therapy: Commonly used in the treatment of anxiety disorders, exposure therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to feared or avoided situations. This helps them confront and overcome their fears, leading to decreased anxiety over time.
- Skill Building: CBT equips individuals with practical coping strategies and problem-solving skills. This empowers them to navigate life’s challenges more effectively and build resilience.
Applications of CBT:
- Depression: CBT has proven to be highly effective in the treatment of depression. By addressing negative thought patterns and promoting behavioral activation, individuals can experience significant improvements in mood and overall functioning.
- Tension issues: CBT is a first-line treatment for various tension problems, which include generalized anxiety ailment, social anxiety sickness, and panic ailment. Exposure remedy inside CBT is especially useful in treating phobias and obsessive-compulsive sickness (OCD).
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): CBT, especially in the form of trauma-focused therapy, has shown success in alleviating symptoms of PTSD by helping individuals process and reframe traumatic memories.
- Eating Disorders: CBT is widely used in the treatment of eating disorders like bulimia nervosa and binge-eating disorder.It addresses distorted body photograph and unhealthy consuming behaviors thru cognitive restructuring and behavioral interventions.
Persistent ache control: CBT is increasingly more used as a part of a multidisciplinary technique to handling persistent pain. - Chronic Pain Management: CBT is increasingly used as part of a multidisciplinary approach to managing chronic pain. It helps individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms, reducing the impact of pain on their daily lives.

Conclusion:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy stands as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with a range of mental health challenges. Its evidence-primarily based nature, aim-orientated technique, and flexibility make it a powerful tool within the arms of therapists and a supply of empowerment for those searching for to beautify their intellectual well-being. As research continues to unfold, CBT remains at the leading edge of innovative and powerful mental health interventions, presenting a pathway to high-quality change and lasting.