Introduction:
Erik Erikson, a renowned German-American developmental psychologist, made significant contributions to the field of psychology with his theory of psychosocial development. Erikson proposed that individuals go through a series of stages, each characterized by a unique psychosocial crisis that must be successfully resolved for healthy personality development. These stages span the entire lifespan, from infancy to old age, and provide a framework for understanding the complexities of human development.

Early Life and Education:
Erikson’s early life experiences greatly influenced his later work. Born to a Danish mother and unknown father, Erikson struggled with questions of identity and belonging. He initially trained as a psychoanalyst and later worked with Anna Freud at the Vienna Psychoanalytic Institute. His interest in the role of culture and society in shaping human development led him to explore areas beyond traditional psychoanalytic theory.
Psychosocial Development Theory:
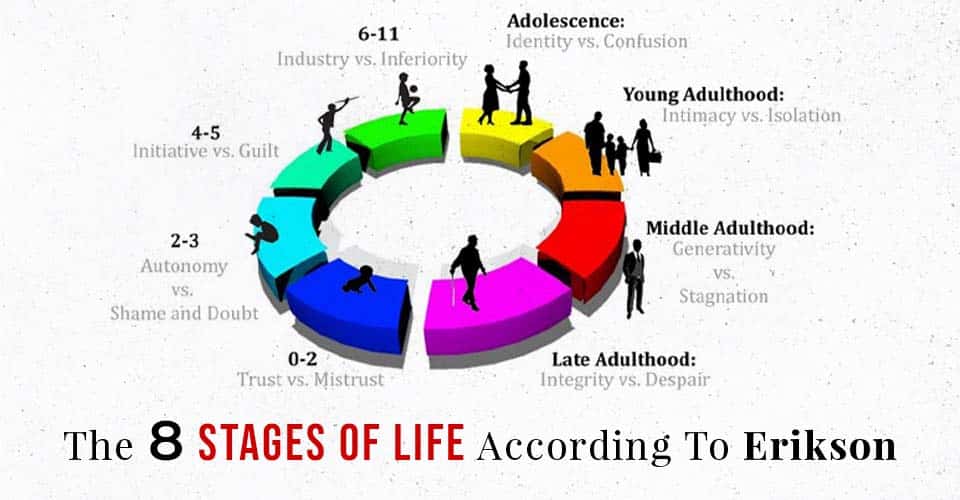
Erikson’s most renowned contribution is his eight-stage theory of psychosocial development, which spans the entire human lifespan. Each stage is characterized by a unique psychosocial crisis, representing the challenges individuals face and the virtues they can develop by successfully resolving these crises.
- Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy)
- Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Early Childhood)
- Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool)
- Industry vs. Inferiority (Elementary School)
- Identity vs. Role Confusion (Adolescence)
- Intimacy vs. Isolation (Young Adulthood)
- Generativity vs. Stagnation (Middle Adulthood)
- Integrity vs. Despair (Late Adulthood)
Erikson’s holistic approach considers both individual and social influences on development, emphasizing the importance of cultural context in shaping identity.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795740-article-erik-eriksons-stages-of-psychosocial-development-5ac3df9e875db90037ffa803.png)
-
Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy: 0-1 year):
The first stage centers around the infant’s relationship with their primary caregiver. Trust is established when the caregiver consistently meets the child’s needs, fostering a sense of security and predictability. Failure to establish trust can lead to mistrust and a fundamental sense of insecurity, potentially impacting future relationships.
-
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Early Childhood: 1-3 years):
During this stage, toddlers begin to assert their independence by exploring their environment. If caregivers encourage autonomy within reasonable limits, the child develops a sense of control and self-confidence. Conversely, excessive criticism or restrictions can lead to shame and doubt, hindering the development of autonomy.
-
Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool: 3-6 years):
Preschoolers start to take initiative in activities and social interactions. Successful resolution of this stage results in a sense of purpose and the ability to plan and initiate tasks. However, if caregivers are overly restrictive or critical, children may develop feelings of guilt, impeding their ability to take healthy initiative.
-
Industry vs. Inferiority (Elementary School: 6-12 years):
During the elementary school years, children engage in learning and social activities. Success in this stage is marked by the development of competence and confidence in one’s abilities. Conversely, failure to master tasks or constant feelings of inadequacy may lead to a sense of inferiority.
-
Identity vs. Role Confusion (Adolescence: 12-18 years):
Adolescence is a crucial period of identity formation. Teens explore their roles, values, and beliefs, seeking to establish a clear sense of self. Successfully navigating this stage results in the development of a strong and coherent identity, while failure can lead to confusion about one’s place in the world.
-
Intimacy vs. Isolation (Young Adulthood: 18-40 years):
Young adults focus on building intimate relationships and commitments. Establishing healthy connections with others leads to the development of intimacy, while fear of or social isolation can result in emotional detachment and a sense of loneliness.
-
Generativity vs. Stagnation (Middle Adulthood: 40-65 years):
During middle adulthood, individuals seek to contribute to society and future generations, whether through parenting, work, or community involvement. Those who succeed in this stage experience a sense of generativity and fulfillment, while those who do not may feel stagnant and unfulfilled.
-
Integrity vs. Despair (Late Adulthood: 65+ years):
In the very last degree, individuals reflect on their lives and accomplishments. Successfully resolving this stage leads to a sense of integrity, acceptance of one’s life, and a readiness for death. Failure to achieve this sense of completeness can result in despair and a fear of the inevitable end.

Conclusion:
Erik Erikson’s stages of psychosocial development provide a comprehensive and insightful framework for understanding the lifelong process of human growth and maturation. By exploring these stages, psychologists, educators, and individuals can gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities that each phase of life presents. Erikson’s enduring legacy lies in his contribution to our understanding of the complex interplay between individual development and the social and cultural contexts in which it occurs.

Hi there, the whole thing is going well here and ofcourse every one is sharing facts, that’s really excellent,
keep up writing.
консультации юриста бесплатно для всех вопросов о законодательстве|юридическое обслуживание бесплатно на законодательные темы
Юридическая консультация бесплатно для частных лиц и предприятий по различным вопросам Получи бесплатную юридическую консультацию от бесплатный совет юриста: надежное решение юридических проблем|Получи бесплатное консультирование от опытных юристов по различным проблемам
Бесплатная юридическая консультация для частных лиц
помощь юриста бесплатно по телефону https://www.konsultaciya-yurista-499.ru.
Надежный юрист по наследственным спорам
задать вопрос юристу по наследству http://www.yurist-po-nasledstvu-msk-mo.ru .
protector 3 plus отзывы
https://protector3-plus.ru/
Нужен арбитражный юрист? Вы на правильном пути!|
Профессиональная помощь арбитражного юриста в любой ситуации!|
Затрудняетесь в вопросах арбитражного права? Обращайтесь к нам!|
Лучшие результаты с нами, арбитражный юрист гарантирует!|
Ищете арбитражного юриста, который оказывает услуги максимально дешево? Мы готовы вам помочь!|
Наш опыт и знания позволят найти выход из любой ситуации.|
Помощь на каждом этапе от арбитражного юриста в компании название компании.|
Качественная защита на всех этапах арбитражного процесса.|
Оставьте свои проблемы нас, арбитражный юрист справится со всеми!|
Уникальный опыт и знания – это арбитражный юрист название компании.|
Ищете быстрое решение проблемы? Обращайтесь к нам, название компании.
судебный юрист по арбитражным спорам https://www.arbitrazhnyj-yurist-msk.ru.
Требуется адвокат по разводу? Используйте наши услуги!
Квалифицированный адвокат по разводу: гарантия защиты ваших прав
бракоразводный процесс при наличии http://advokat-po-razvodam-v-mks-i-mo.ru/.
It is a wonderful website with an attractive design. Thank you for the valuable information https://continueright.com/
Разбор случаев отзыва водительского удостоверения: рекомендации автоюриста
авто юрист https://tuvaonline.ru/obrashhaemsja-k-avtojuristu.dhtml .